Digital dermatitis, also known as foot rot or hairy heel warts, is a common infectious hoof disease that affects cattle. Digital dermatitis causes painful lesions on the hooves of cows, leading to lameness and reduced mobility, which can impact their overall health and productivity.
Symptoms of digital dermatitis in cows include red, painful and swollen lesions on the skin around the hooves, accompanied by lameness or limping. Digital dermatitis is typically diagnosed based on clinical signs and physical examinations of the cow’s hooves by a veterinarian or a trained professional.
The Cause of Digital Dermatitis: Treponema Bacteria
The Treponema bacteria play a central role in the development of Digital Dermatitis. These bacteria, thriving in damp and dirty conditions, invade the skin of the hoof, creating painful lesions. Their infectious nature means they can quickly spread within a herd, especially in environments with poor hygiene.
Treponema species are anaerobic bacteria, which means they can survive and multiply in environments with low oxygen levels. They are spiral-shaped and have a flexible outer sheath that allows them to move and penetrate tissues, including the skin and hooves of cattle.
In Digital Dermatitis, Treponema bacteria can enter the hooves through minor cuts or abrasions and cause infection. This leads to the development of characteristic lesions, including painful ulcers and erosions on the hooves’ skin.
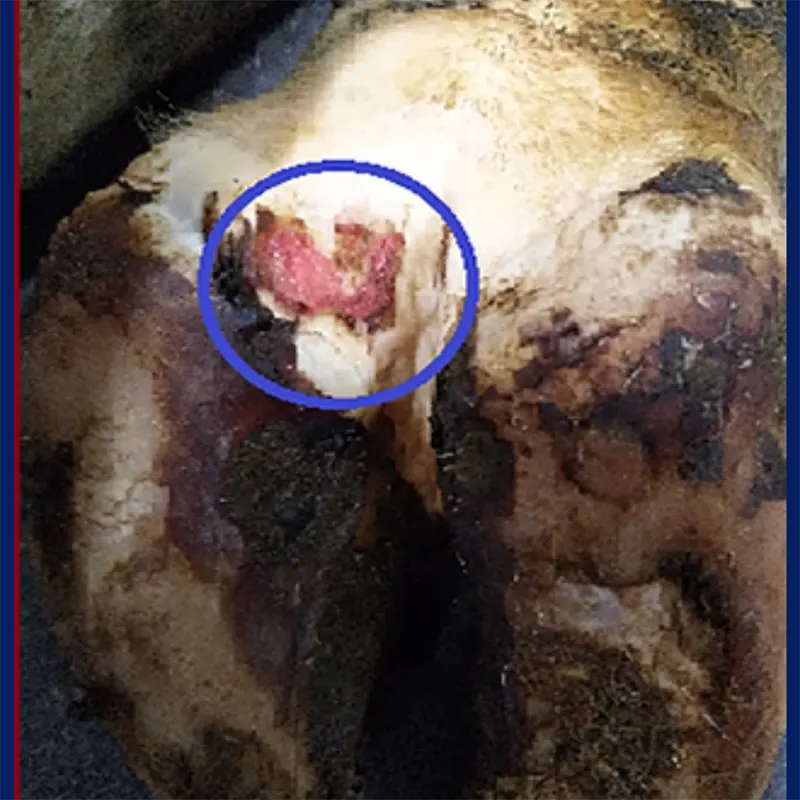
Stages of Digital Dermatitis
Understanding the progression of Digital Dermatitis is vital to effective management. The disease typically evolves through several stages:
- Stage 1 – Proliferative (Hairy) Stage: This is the initial stage of digital dermatitis. The lesion appears as a small, circular, inflamed, and reddened area on the skin near the interdigital space between the claws. It has a moist appearance and may resemble a small ulcer or erosion. The lesion is typically accompanied by swelling and can be painful for the cow.
- Stage 2 – Active Lesion: At this stage, the lesion becomes more pronounced and has a hairy or fibrous appearance. It appears as a raised, cauliflower-like growth on the skin. The lesion is typically grey or black and has a rough texture due to the proliferation of bacteria, particularly Treponema species, and the formation of a protective biofilm. The lesion can cause discomfort and lameness in affected cows.
- Stage 3 – Hyperkeratotic (Warty) Stage: This lesion is characterised by the enlargement and extension of the Stage 2 lesion. It becomes more severe, larger and more painful for the cow. The skin may become ulcerated, and a foul odour can be associated with the infection. The lesion is covered with a thick, greyish, foul- smelling discharge. The lesion may transition to the hyperkeratotic stage, where the skin becomes thickened and wart-like.
- Stage 4: The lesion becomes more severe at this stage, extending deeper into the tissues. The lesion is painful and causes significant lameness in affected cows. The skin becomes thickened, rough, and warty in appearance. It may involve deeper tissues, such as the digital cushion, leading to severe swelling and inflammation.
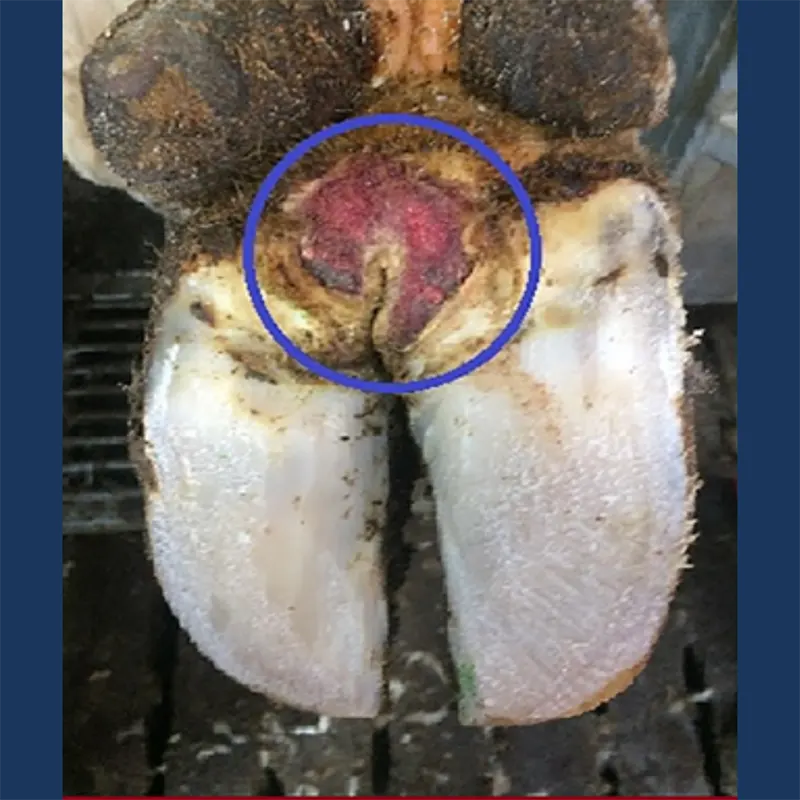
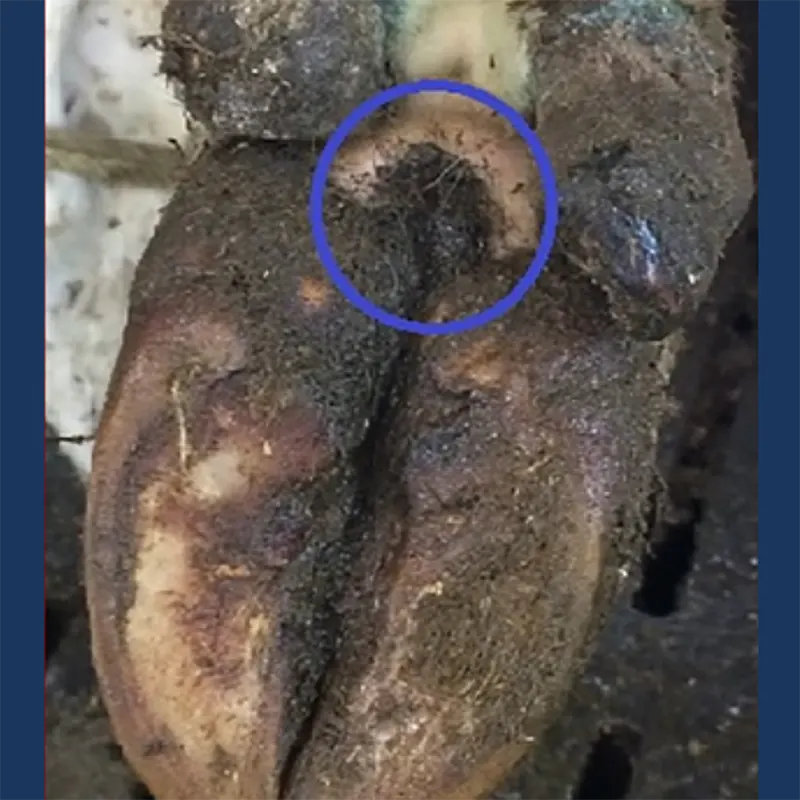
Individual Variations in Progression
It’s important to note that Digital Dermatitis can vary among individual cows and herds. Environmental conditions, herd management practices, and individual cow immunity affect how the disease manifests and progresses. Implementing tailored hoof trimming schedules, maintaining strict hygiene practices, and adhering to comprehensive management protocols are essential in preventing and controlling Digital Dermatitis.
Effective Management Strategies
1. Early Detection and Isolation:
Regular hoof checks are crucial for early detection. Isolating affected cows and administering targeted treatment can prevent the spread of infection.
2. Routine Hoof Care and Maintenance:
Establish a hoof care routine that includes regular trimming and maintenance to ensure hoof balance and health, reducing the risk of infection.
3. Targeted Treatment:
Treat affected cows promptly with appropriate topical antibiotics and bandaging. Consult with a veterinarian for the most effective treatment options.
Preventive Measures
- Maintain Clean, Dry Environments:
Create a clean and dry living environment for your herd to minimise exposure to the bacteria causing Digital Dermatitis. - Effective Footbaths:
Implement footbaths with antibacterial solutions as a preventive measure. Ensure the correct concentration of the solution and change it regularly for maximum effectiveness. - Nutrition and Stress Management:
A well-balanced diet contributes to overall hoof health. Manage stress by providing adequate space, comfortable bedding, and efficient cow traffic flow. - Regular Monitoring:
Keep thorough records of all incidences, treatments, and preventive measures. Review and adjust your strategies regularly based on these insights.
Tips for Effective Management Strategies
Early Detection and Isolation:
- Tip: Immediately isolate affected cows and start targeted treatments.
- Benefits: Controls infection spread, maintaining the health of the entire herd.
Routine Hoof Care and Maintenance:
- Tip: Implement a consistent hoof care program with regular trimming.
- Benefits: Keeps hooves balanced and healthy, reducing infection risks.
Targeted Treatment:
- Tip: Apply recommended treatments effectively.
- Benefits: Ensures quick recovery and reduces discomfort in affected cows.
Maintain Clean, Dry Environments:
- Tip: Keep cow living areas hygienic and free from moisture.
- Benefits: Lowers bacteria growth, enhancing herd health.
Effective Footbaths:
- Tip: Use footbaths regularly with appropriate antibacterial solutions.
- Benefits: Actively prevents Digital Dermatitis, maintaining hoof health.
Nutrition and Stress Management:
- Tip: Provide balanced nutrition and stress-free conditions.
- Benefits: Boosts overall health, supporting hoof health and disease resistance.
Regular Monitoring:
- Tip: Maintain detailed records of treatments and hoof health.
- Benefits: Facilitates early detection of issues for timely intervention.
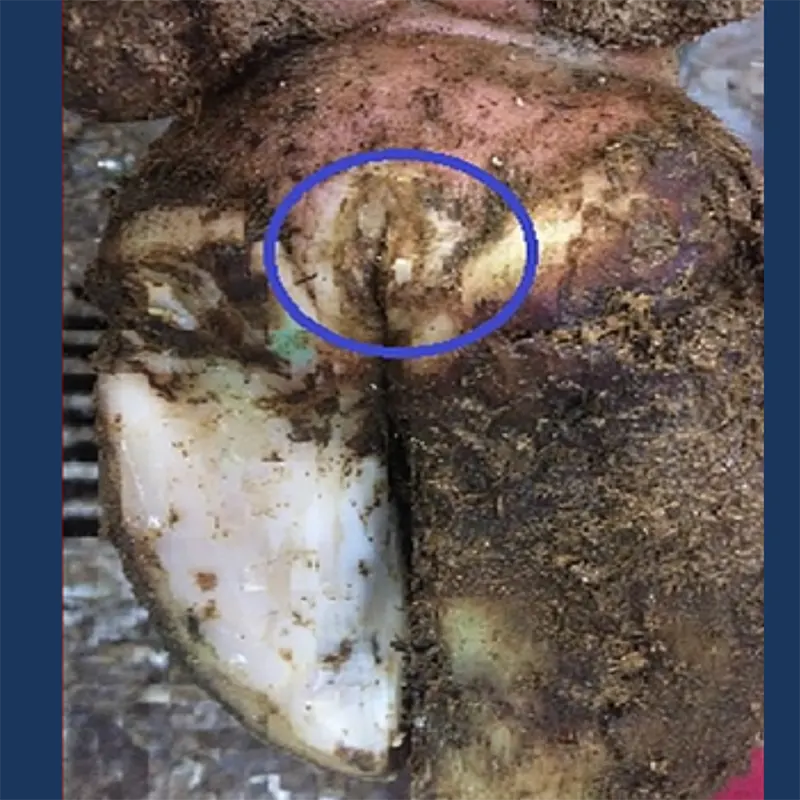
Digital Dermatitis management requires a multifaceted approach that includes understanding the disease, early detection, effective treatment, and rigorous preventive measures. By maintaining high hygiene standards, implementing regular hoof care routines, and staying vigilant, you can significantly mitigate the impact of this disease on your dairy operation.




